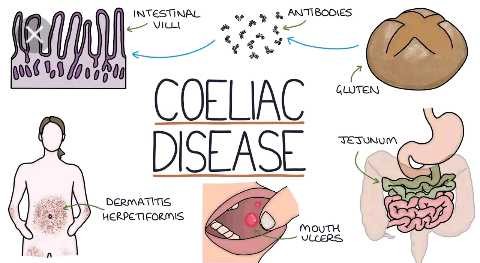
Ciliac disease also called celiac sprue, is a hereditary autoimmune intolerance to gluten. The consumption of foods containing gluten- a protein found in rye, barley and wheat- triggers an immune response that damages the villi of the small intestine and prevents it absorbing nutrients.
Apart from occurring naturally in the wheat plant and in some other grains, gluten can be extracted, concentrated and added to foods to add protein, flavour and texture. It’s also used as a binding agent to give processed foods shape and hold them together.
Celiac disease damages the small intestines lining, causing inflammation and malabsorption. Due to this, individuals with the condition suffers from malnutrition, osteoporosis, nervous system impairment, seizures, birth defects, pancreatic diseases, infertility and miscarriages.
The common symptoms, include abdominal pain, bloating, joint or bone pain, constipation, diarrhoea, fatigue, headache, mouth ulcers, nausea’s and anaemia among others.
In children, the condition manifest itself around six to nine months of age when they are introduce to cereals during complementary feeding and can be easily be mistaken with lactose intolerance or irritable bowel syndrome due to their similarities in symptoms.
Currently, there is no known cure for celiac disease, but it can be managed by permanently adopting a completely gluten free diet. Removing gluten foods from the diet relieves symptoms and allows the intestinal lining to heal and begin absorbing nutrients. It’s advisable to avoid gluten containing foods unless they are labeled as gluten free versions.
Please like share and comment.
source; https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/celiac-disease/
Content created and supplied by: @andy (via Opera
News )