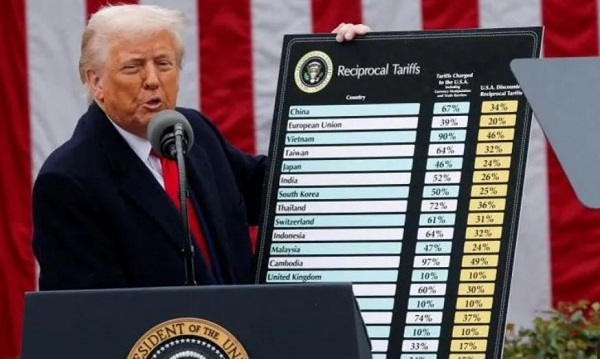
A federal court on Wednesday ruled that President Donald Trump overstepped his authority to impose sweeping tariffs that have raised the cost of imports for everyone from giant businesses to everyday Americans.
But the administration immediately appealed the decision on Wednesday night, leaving the situation uncertain for consumers and companies and potentially prolonging the battle over whether Trump’s import duties will stand – and possibly reshape the global economy.
A three-judge panel at the US Court of International Trade, a relatively low-profile court in Manhattan, stopped Trump’s global tariffs that he imposed citing emergency economic powers, including the “Liberation Day” tariffs he announced on April 2.
It also prevents Trump from enforcing his tariffs placed earlier this year against China, Mexico and Canada, designed to combat fentanyl coming into the United States.
The court ruled in favor of a permanent injunction, potentially grinding Trump’s global tariffs to a halt before “deals” with most other trading partners have even been reached. The court ordered a window of 10 calendar days for administrative orders “to effectuate the permanent injunction.” That means the bulk – but not all – of Trump’s tariffs would be put in a standstill if the ruling holds up in appeal and, potentially, with the Supreme Court.
The order halts Trump’s 30% tariffs on China, his 25% tariffs on some goods imported from Mexico and Canada, and the 10% universal tariffs on most goods coming into the United States. It does not, however, affect the 25% tariffs on autos, auto parts, steel or aluminum, which were subject to Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act – a different law than the one Trump cited for his broader trade actions.
Stock futures surged on the ruling. Dow futures rose nearly 500 points, or 1.1%. The broader S&P 500 futures were up 1.4%, and Nasdaq futures were 1.6% higher in afterhours trading.
The lawsuit was filed by the libertarian legal advocacy group Liberty Justice Center in April and represented wine-seller VOS Selections and four other small businesses that claimed they had been severely harmed by the tariffs. The panel came to a unanimous decision, publishing an opinion on the VOS suit and also one by twelve Democratic states brought against the Trump tariffs.
“We won – the state of Oregon and state plaintiffs also won,” Ilya Somin, a law professor at Scalia Law School, George Mason University and plaintiff lawyer, said to CNN immediately after the ruling. “The opinion rules that entire system of liberation day and other IEEPA (International Emergency Economic Powers Act) tariffs is illegal and barred by permanent injunction.”
Declaring a national economic emergency
On April 2, Trump announced his “reciprocal” tariffs, imposing significant levies on imports from some of America’s closest trading allies – though he soon after implemented a 90-day pause on April 9. He left in place “universal” 10% tariffs on most goods coming into the United States.
Trump implemented these tariffs without Congress by invoking the International Emergency Economic Powers Act, which gives the president the authority to act in response to unusual and extraordinary threats. But the law does not include any mention of tariffs as a potential action the president can take once IEEPA is invoked.
Trump also cited IEEPA in his 20% tariffs on China and 25% tariffs on many goods from Mexico and Canada designed to target fentanyl trafficking into the United States.
But the Trump administration has not met that criteria for an emergency, the plaintiffs alleged. The lawsuit also alleges IEEPA doesn’t give the president the power to enact tariffs in the first place, and even if it was interpreted to, it “would be an unconstitutional delegation of Congress’s power to impose tariffs,” according to a statement.
The court concurred in its ruling that Trump lacked the authority to impose those tariffs even after declaring a national emergency.
“IEEPA does not authorize any of the worldwide, retaliatory, or trafficking tariff orders,” the panel of judges said in their order Wednesday. “The worldwide and retaliatory tariff orders exceed any authority granted to the President by IEEPA to regulate importation by means of tariffs. The trafficking tariffs fail because they do not deal with the threats set forth in those orders.”
‘Surprising and spectacular’ decision
White House spokesperson Kush Desai said in a statement that: “It is not for unelected judges to decide how to properly address a national emergency. President Trump pledged to put America First, and the Administration is committed to using every lever of executive power to address this crisis and restore American Greatness.”
White House deputy chief of staff for policy Stephen Miller was blunter, posting on X that “The judicial coup is out of control” in response to the news.
Gary Clyde Hufbauer, a nonresident senior fellow at the Peterson Institute for International Economics, called it a “surprising and spectacular decision.”
“The reason it’s a surprise is that if you look at past cases where plaintiffs have tried to challenge the presidential use of extraordinary authority under various laws, the plaintiffs have always lost against the government,” Hufbauer said in an interview with CNN.
“All the president had to do was say, ‘national security,’ or ‘national emergency.’ Those are magic words.”
The decision could help small businesses across America, many of which had been struggling with the jump in costs from tariffs.
“This is potentially – with that word choice underscored – a significant policy pivot point should it hold up for both the economy and the quiet majority inside Congress that does not support current trade policy,” Joe Brusuelas, RSM US chief economist, wrote in an email to CNN Business. “In particular, this would provide a huge relief for small and medium sized firms that neither have the margins nor the financial depth to absorb the tariffs on a sustained basis.”
The plaintiffs are hopeful they can gain some certainty for their businesses, Jeffrey Schwab, lead attorney for the Liberty Justice Center, told CNN’s Kaitlan Collins Wednesday.
“They’re hopeful that these will be upheld by the appellate court so that they can continue their businesses with the certainty of what’s going to happen rather than the uncertainty of not knowing what the tariff rate is at any given time and whether it will change,” Schwab said.
“Obviously this is a very important case, not only because of the tremendous economic impact that it has on everybody, but particularly business and our businesses, but also because of the tremendous power grab that the administration is claiming here,” Schwab continued. “He can’t just assert unlimited authority to tariff whenever he wants.”
Potentially headed to the Supreme Court
The Department of Justice lawyers argued that the tariffs are a political question – meaning it’s something that the courts can’t decide.
But the plaintiffs noted IEEPA makes no mention of tariffs.
“If starting the biggest trade war since the Great Depression based on a law that doesn’t even mention tariffs is not an unconstitutional usurpation of legislative power, I don’t know what is,” Somin said in April.
Separately, and using similar arguments, twelve Democratic states sued the administration in the same court for “illegally imposing” tax hikes on Americans through the tariffs.
“We brought this case because the Constitution doesn’t give any president unchecked authority to upend the economy. This ruling reaffirms that our laws matter, and that trade decisions can’t be made on the president’s whim,” Oregon Attorney General Dan Rayfield said in a statement Wednesday.
The judges on the Manhattan panel were each appointed by a different president. Judge Jane Restani was appointed to the US Court of International Trade by President Ronald Reagan. Judge Gary Katzmann was appointed to the court by President Barack Obama. Judge Timothy Reif was appointed by President Trump.
The immediate higher court is the federal circuit, though it could potentially go right to the Supreme Court.
The United States Court of International Trade is a federal court in Manhattan that handles disputes over customs and international trade laws.